By Arunprasath Ramamoorthy (Samsung), Sapan Pramodkumar Shah (Nokia), Basu Pattan (SA6 Vice-chair, Samsung), Atle Monrad (SA6 Chair, Interdigital)
Published December 2025, in Highlights Issue 11
The term Metaverse refers to the immersive experiences in a virtual world where users can interact with each other and/or interact with digital objects. Metaverse in diverse industry sectors offers new experiences, products and services that emerge through Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR) and eXtended Reality (XR) technologies. With metaverse, physical spaces can be converged with virtual spaces through spatial maps and augmented with digital objects like spatial anchors - to provide users with enriched information of objects in physical space.
The users in this virtual world are represented by avatars (which is one of the digital assets of the user). Spatial anchors, Avatars and Spatial maps play a significant role in enabling mobile metaverse services. Healthcare, Consumer Retail, Gaming, Communications and Entertainment are some of the industries which are bound to be benefitted to a larger extent by adopting mobile metaverse services.
Use cases and Requirements
3GPP SA WG#1, as part of FS_Metaverse study in 3GPP TS 22.156, has looked at various use cases and identified the service and performance requirements for diverse service enablers - to enable mobile metaverse services. Some of the application enablement requirements are:
Localized mobile metaverse service – to provide an immersive experience or enriching user experience with contextually appropriate digital layers and media based on the user’s location and interest (e.g. spatial anchors).
Support for Avatar as Digital asset service – to manage avatars as the digital representation of users. Requirements related to format, management, and storage of digital assets will improve the interoperability of digital assets across various mobile metaverse platforms.
Exposure of mobile services – meeting requirements related to providing access to spatial anchors, spatial maps and digital assets for mobile metaverse services
Application Enablement within the 3GPP System
Figure 1 illustrates the service frameworks and application enablers specified by 3GPP SA WG#6, to enable an efficient and simplified adoption of vertical applications over the 3GPP system.
The layered representation illustrates how the services offered at each layer consume the lower layer services to offer added value to the layers above - through service abstraction. The SA WG#6 defined application enablers offer value added services to the application layer, leveraging the core network and OAM & charging services specified by 3GPP SA WG#2 and SA WG#5 respectively. The application enablers, in general, are access agnostic.
Figure 1: Application Enablement within the 3GPP system
Mobile Metaverse Enablers
Mobile metaverse services are immersive and integrated into user's conventional experiences. Such immersive experiences are location-specific (3D locations in the physical world) and enriched with services like spatial maps, spatial anchors, digital assets etc. The Spatial map is a collection of information corresponding to the physical space, incorporating the information gathered from sensors concerning the characteristics of the forms in that physical space. Spatial maps enable the creation of the digital representation of the physical spaces.
The spatial anchor is an association between a location in space (three dimensions) and service information for offering immersive experience services. A digital asset is digitally stored information that is uniquely identifiable and can be used to realize value according to their licensing conditions and applicable regulations. Examples of digital asset are avatars, software licenses, gift certificates, tokens and files (e.g., music files), etc. The commonly used digital asset in metaverse services is an avatar. An avatar is a digital representation specific to media that encodes facial (possibly body) position, motions and expressions of a person or a software generated entity. Avatars enable the users in the virtual world to interact with each other for participation or collaboration in various immersive services (e.g, gaming, events).
3GPP SA WG#6 has specified these mobile metaverse enablers to support the metaverse applications, including application layer architecture, procedures and information flows. The Spatial Anchors (SAn) and the Spatial Map (SM) services are specified in 3GPP TS 23.437, while Avatars as Digital Assets (DA) are specified in 3GPP TS 23.438.
The generic architecture of these mobile metaverse enablers is illustrated in Figure 2 below:
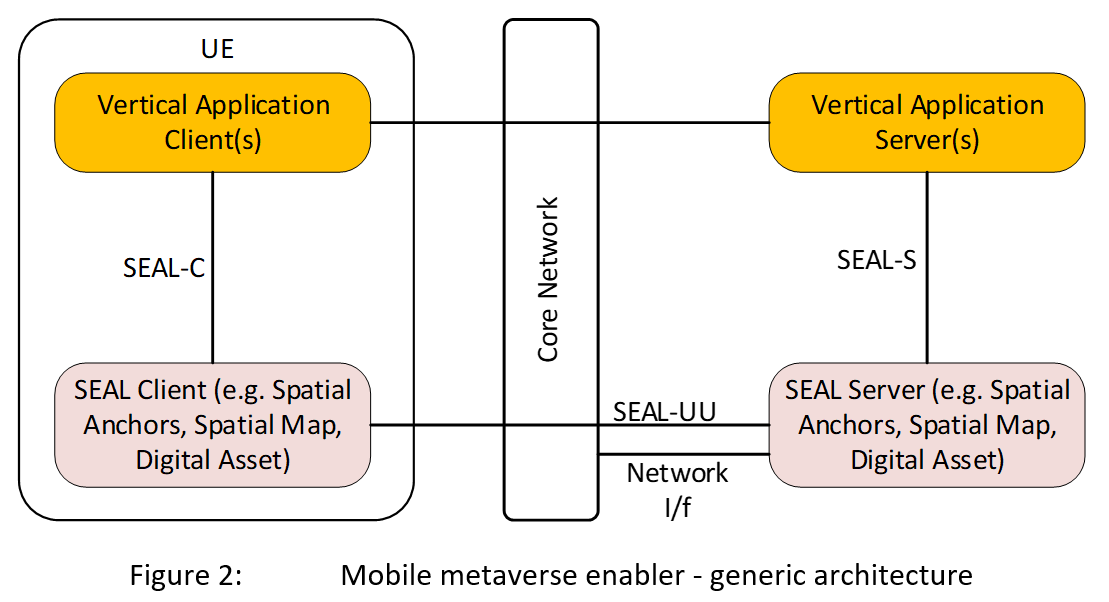
This application enabler layer architecture for mobile metaverse services implements the SEAL (Service Enabler Architecture Layer) architecture as specified in 3GPP TS 23.434. Mobile metaverse services specified in 3GPP TS 23.437 and 3GPP TS 23.438 are SEAL services. The VAL (vertical application layer) client and VAL server are the vertical application client and vertical application server respectively providing immersive application services to the user. The SEAL client and SEAL server provides the client and server side functionalities respectively for managing the mobile metaverse services (e.g. SAn, SM and DA) for the vertical applications. The VAL client and SEAL client interact over SEAL-C interface. The interface between SEAL Client and SEAL Server is SEAL-UU. The SEAL server interacts with the VAL server over the SEAL-S interface. The SEAL-UU and SEAL-S implements procedures to manage mobile metaverse services (e.g. SAn, SM and DA).
Details about services offered by mobile metaverse enabler are explained below:
Spatial Anchors (SAn) service
The Spatial Anchors services are offered by the SEAL SAn server to the service consumers (i.e, VAL server, VAL client). The Spatial Anchors services offer the capabilities to manage the spatial anchors belonging to the vertical application layer (VAL) entities that are offering metaverse services. The functional model of Spatial Anchor service is illustrated in Figure 2.
The SEAL client is a SEAL SAn client and the SEAL server is a SEAL SAn server. SAn client and SAn server support the application layer entities that offer metaverse services for managing the spatial anchors. Each spatial anchor is associated with the profile which contains information related to the spatial anchor such as identifier, position information, services information, expiry time, etc of the spatial anchor. Spatial anchors can be grouped, which refers to the collection of spatial anchors based on locations (e.g. Museums in a city) or objects (e.g. items in a shop). Spatial anchor group management services allows organizing the spatial anchors into groups based on logical relationships so owners can manage them efficiently.
The functionalities supported by spatial anchors service are:
- Management of Spatial anchors: Provide the operations support for managing the spatial anchors by the spatial anchor providers/owners (e.g, Metaverse Application server). The authorized entities can Create, Retrieve, Update and Delete the spatial anchors. Each spatial anchor has a spatial anchor profile which characterizes the information (e.g. position, service, access control) related to spatial anchor and are maintained at the SAn server.
- Spatial Anchor Discovery: Enables the service consumer to discover the available spatial anchors based on the discovery filters (e.g. area of interest, associated service).
- Spatial Anchor Group Management: Enables the service consumer to manage spatial anchors as groups.
- Spatial Anchor subscription: Enables the service consumer to subscribe to events related to creation, modification, update and removal of spatial anchors, periodically fetch list of spatial anchors fulfilling the discovery criteria filters or discovery of spatial anchors within the range of the UE or discovery of spatial anchors when a UE enters or exits the range of interested spatial anchors provided consumers.
- Spatial Anchor Usage reporting: Enables the spatial anchor owners (e.g., VAL server)/providers to receive the insights about the usage of their spatial anchors by the consumers. These insights are helpful to the spatial anchor owners/providers in better planning and management of the spatial anchors.
Spatial Map (SM) service
The Spatial map service offers the capabilities to the vertical application layer entities (VAL server, VAL client) for managing the spatial maps. The Spatial map management functional model is illustrated in Figure 2.
The SEAL client is a SEAL SM client and the SEAL server is a SEAL SM server. The main functional entities are SM client and SM server which provides client and server side functionalities respectively for managing spatial map for the vertical applications. The spatial map service also supports the spatial localization service through which SEAL SM server, identifies all users/UEs localization along with their three-dimensional location and pose in the spatial map based on the request from the vertical application layer.
For creating and managing the spatial map, it is required to get the data from various sources like cameras or sensors. Spatial map service provides a mechanism for the data sources to register with the enabler layer with the information like the type of data they offer and their availability period etc. Application layer when creating the spatial map can discover the available spatial map data sources through the SM server spatial map services and connect to the data sources to fetch the data required for constructing the spatial maps. Spatial map capable application servers (SMAS) are application servers which can offer spatial map service. SMAS can also register with the SM server with the list of spatial maps they support, coverage area of each of the spatial map, media format of the spatial maps etc. Spatial map service consumers can discover and utilize these readily available spatial maps when required. Below are the functionalities supported as part of spatial map services:
- Management of Spatial maps: Provides the operations support for enabling the management of spatial maps by the vertical application layer entities.
- Spatial map discovery: The service consumers can discover the spatial maps available, based on certain criteria, such as an area of interest, the location of consumer, based on the spatial map media formats, based on the spatial map layer information.
- Spatial map subscription: The service consumer can subscribe to and receive notification of events such as list of objects that are added or deleted, when their velocity or position changes, changes to the spatial map layers associated with the spatial map, spatial map is created and ready to use.
- Spatial localization services: Enables the service consumer to identify the users/UEs along with their three dimensional location and pose in the interested area of the spatial map.
- Spatial map data source registration and discovery: Entities capable of providing data that is useful for creation and rendering of the spatial map, can register with SM server as spatial map data source. These entities also provide their capabilities, availability and type of data they produce etc. The VAL servers can discover the available spatial map data sources from SM server, based on certain criteria information such as area of interest, availability, mobility of the data source, etc.
- SMAS (SM capable Application Sever) registration and discovery: Application servers can register with the SM Server with the information of their spatial maps, their coverage area, availability information and connectivity information. The service consumers can discover the end point information of the spatial map application servers, from the SM server.
Digital Assets (DA) Service
To ensure a seamless user experience across metaverse services, network operators offer digital asset management services that allow users to certify certain information, such as IDs. These services support multiple user identities, each representing different aspects of the user's life, such as their professional role and private life. As a result, each user identity can have its own set of information stored in the associated digital asset profile.
Users can be associated with one or more digital assets like Avatars, software licenses, files, etc. Applications like metaverse services can utilize the digital assets related to users, and the users can benefit from having the use of their digital assets between various metaverse services/platforms in an interoperable way. Digital assets service, as specified by 3GPP SA WG#6 in 3GPP TS 23.438, enables management and usage of digital assets to support metaverse services in a secure and controllable way. Digital asset is represented as a combination of digital asset profile along with associated media. The digital asset profile consists of digital asset specific configuration and parameters (e.g. ID, type, allowed locations and access control) applicable to one or more application(s). A digital asset profile can be associated with one or more VAL user(s). The functional model of Digital Asset service is illustrated in Figure 2. The SEAL client is SEAL DA client, the SEAL server is SEAL DA server. The following functionalities are supported for Digital asset service:
- Digital asset profile management: Enables a consumer (VAL server or DA client) of digital asset service to be able to manage (Create, Retrieve, Update and Delete) a digital asset profile.
- Digital asset discovery: Enables a DA client to discover digital assets available in the digital asset service.
- Digital asset media management: Enables a consumer (VAL server or DA client) of digital asset service to manage the media related to digital asset profile.
Advantages
Generally, the services defined at the application enabler layer supports rapid development and deployment of vertical applications. Mobile metaverse services, which can be offered by several MNOs, aims to support faster development of metaverse services at global scale. Mobile metaverse enablers can ensure a seamless user experience across multiple metaverse services without worrying about the interoperability issues by utilizing the common and standard enabler services specified by 3GPP SA WG#6 to manage digital assets, spatial maps and spatial anchors. Considering the diversified portfolio (e.g. gaming, healthcare, virtual offices, virtual concerts/events) of metaverse services, the simple mobile metaverse enabler has high potential to attract more application developers and thereby fostering innovation and monetization. It is expected that these metaverse enablers will help accelerate new Service APIs offering of other SDOs (e.g. CAMARA, Metaverse Standards Forum (MSF)) to support Metaverse services addressing customer base beyond mobility.
Future Plan and Next Steps
Currently 3GPP SA WG#6 is discussing the work areas to focus on as part of the 6G release cycle. Digital twins, sensing services, AI / ML are all potential work areas set to play a role in enhancing immersive experiences offered by mobile metaverse services.


 Technology
Technology