By: Mohammad R. Shikh-Bahaei, Professor of Telecommunications King’s college London
First published June 2025, in Highlights Issue 10
One6G are the newest Market Representation Partner in 3GPP, having joined the project in November 2024. In this article, Professor Shikh-Bahaei looks at how important it is for 6G standards to meet the needs of the e-Health and Robotics verticals.
The one6G Association is an international non-profit organization dedicated to evolving, testing, and promoting next-generation cellular and wireless communication solutions. one6G seeks to accelerate the adoption and market penetration of advanced technologies that meet societal and industry-driven demands for enhanced connected mobility. Founded in March 2021, one6G brings together experts from academia, industry, and public institutions looking forward to a 6G ecosystem with the capabilities to improve the quality, reduce costs and expand reach of healthcare services.
For robotic systems, one6G envisages that 6G has the potential to increase the reliability, capability and operational efficiency of mobile robots at lower complexity.
Potential impact of 6G on E-Health domain:
Healthcare systems require continuous optimization in order to reduce costs and improve quality of services. So far, medical treatment decisions are based on treatment results of a large number of similar patients. This typically leads to generalized and costly treatments that do not account for the needs of each individual patient.
The 6G communication ecosystem is anticipated to facilitate precise modeling of individual treatments, enhance the interconnection between different medical data sources and models of all stakeholders (e.g., patients, doctors, devices and robots), as well as strengthen the capabilities of mobile robotic systems in the entire treatment process with improved connectivity, sensing, and intelligence services. To enable this vision, one6G has identified the following four usage scenarios in e-Health domain, and is working toward detailed analysis of these.
Medical Robotics Applications: The increasing demand of healthcare services and pressing shortage of healthcare personnel call the need for more capable medical robotic systems for caregiving tasks. These entail robotic systems that, among other capabilities, guarantee safety in close proximity to humans, and context-awareness of the health situation of patients to perform context-sensitive actions (e.g., actions sensitive to distress or disease of a patient).
Vital Sign Wireless Sensing: Vital signs are conventionally measured with fixed instruments such as electrocardiographs (ECG) which are wired to the patient, limiting patients’ mobility. Wireless sensing can be used to reliably derive health information of patients to improve quality of patients’ lives by not limiting mobility and facilitating proactive actions when healthcare personnel is overloaded.
Medical Data & Model Sharing: The amount of sensitive data generated by healthcare systems is rapidly increasing, and developments in AI/ML can securely exploit these data. There is a need to securely and in a timely manner exchange information between health sensors/models and high-performance computing stations located in-premises, in-network or at trusted/secure third-party providers.
Immersive & Ubiquitous Treatment: Currently, there is a massive burden on global healthcare systems due to mental health diseases. The proliferation of new consumer devices such as extended reality devices and wearables together with AI/ML technologies enables new immersive experiences for remote treatments (e.g., psychotherapeutic) as well as expanding reach of patient monitoring. These 6G technologies can also enable a range of interventional procedures for patients in remote locations.
Potential impact of 6G on Robotics:
It is expected that humanoid robots, as well as robots of other embodiments, will play a huge role in society in the coming years and decades. However, robots face numerous challenges when operating in real world scenarios – such as efficient communication of multi-modal sensor data, interoperability between robot platforms, limitations due to battery life, and more. These challenges must be solved before the future vision of robots as workers, caregivers and human assistants can be realized.
The 6G ecosystem can act as an enabling technology for robotics systems, through enhancements to communications protocols, offering communication-based services to connected robotic devices, enabling computational offloading for reduced energy usage, and by leveraging wireless sensing capabilities. To illustrate the potential of 6G technology applied to robotics, one6G identified a number of use cases in the intersection of 6G and robotics, including the following three highlighted use-cases.
Wireless Sensing for Robotic Search and Rescue: In disaster scenarios such as earthquakes, it can be beneficial to augment the efforts of human search and rescue crews with robots such as mobile robots, quadrupeds and in the future potentially humanoids. However, robots benefit from a “map” of the environment for efficient navigation, which in the event of infrastructure damage to roads and buildings may be out of date. Wireless sensing, which can be effective at longer range than traditional robotic sensors, can be integrated with robotic navigation systems to provide an initial map of the environment, improving the efficiency of search and rescue efforts.
Communication-Aware Robotic Navigation & Motion Planning: A key benefit of robots is the ability to operate in environments which are remote, dangerous or otherwise difficult for human workers – for example, a quadruped robot deployed on an offshore platform for remote inspection. In such scenarios, communication infrastructure is typically limited, and therefore robots may be limited in their ability to transfer high volumes of data, such as RGB image streams. Integration between 6G and robotic motion planning system can enable robots to consider radio coverage conditions in their planning algorithms, thus navigating in a “communication-aware” way to ensure successful data transfer.
Wireless Sensing for Enhanced Physical Interaction: Physical interaction is a hugely important (and challenging) problem that is required to be solved to enable robots to operate safely in real-world conditions. Robots typically can support diverse range of on-board sensing capabilities to deal with physical interaction tasks, including cameras, force/torque sensors, and touch or haptic based sensing. However, wireless sensing can provide a key benefit to the existing robot sensor suite by leveraging close-range high frequency ISAC to determine the material properties of objects without requiring physical interaction. This could be especially relevant for robots which are tasked with handling irregular objects in real-world scenarios, such as humanoid robots.
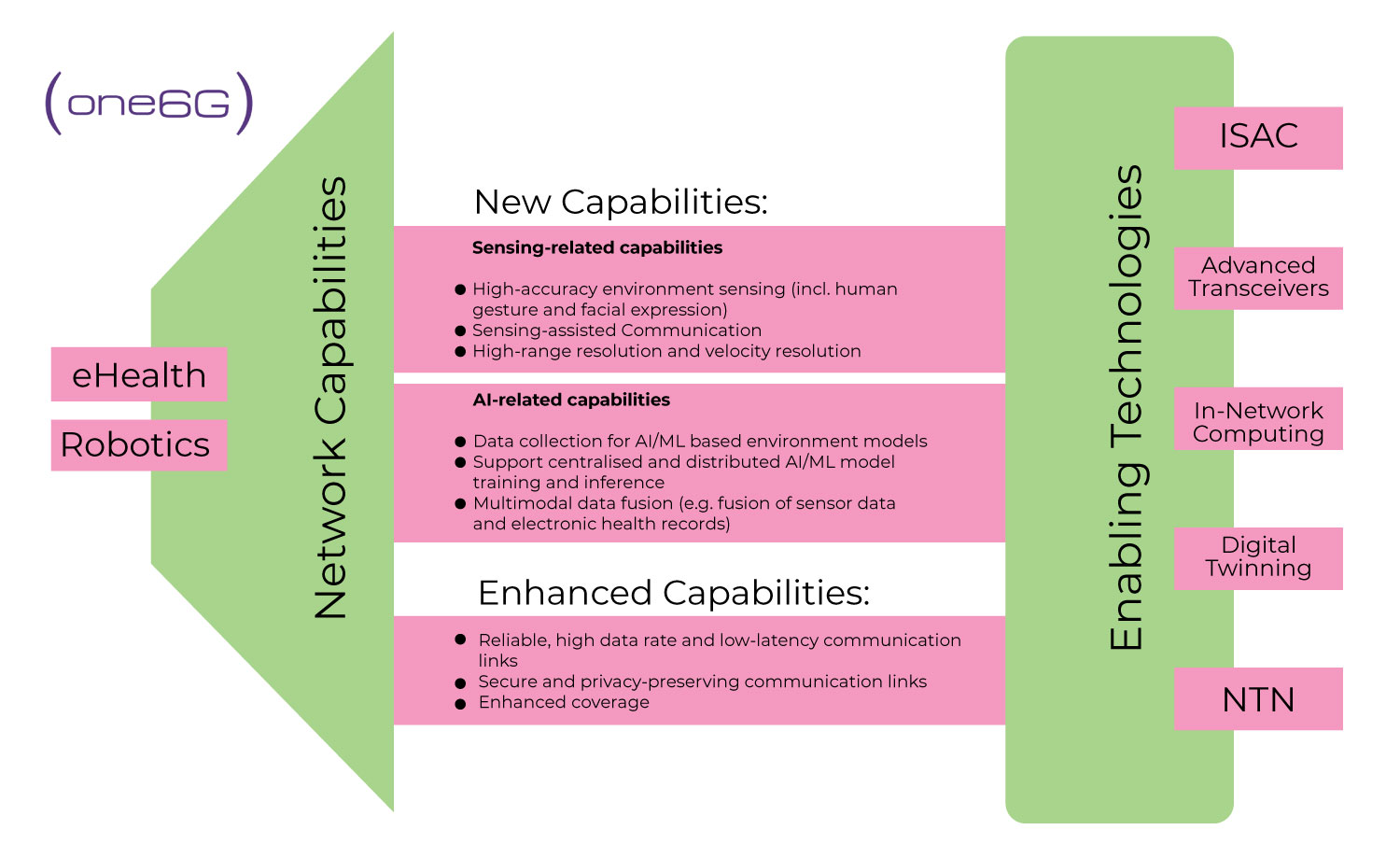
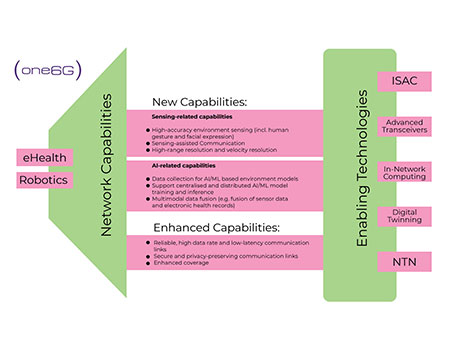
Figure A. Capabilities and enabling technologies for the support of e-Health and Robotics applications.
Identified Capabilities and Enabling Technologies for e-Health and Robotics domains:
The sensing-related and AI-related new capabilities, as well as the enhanced capabilities and the enabling technologies for e-Health and Robotics are highlighted in Figure A.
Other requirements (functional and operational) for 6G to cater use cases in the e-Health and Robotics domain include:
- Dependability: Healthcare, industrial and consumer environments require reliable and high availability of communication and sensing across outdoor and indoor environments.
- Safety: Collaborative tasks between mobile robots and humans should be safe from the outset. The 6G system shall trigger/perform counter measures against potential risks and hazards to guarantee safety. One example is to trigger protective stop with 3GPP sensing for unintended robot motions as per ISO standards.
- Resilience: Communication and sensing infrastructure should be robust to jamming, eavesdropping and natural events.
- Simplified Operations: Professionals in healthcare and industrial environments shall be able to interact with 6G system with ease.
Although the network capabilities broadly overlap to enable uses cases of different vertical domains, detailed analysis of the use cases reveal some unique and specific network requirements. Given that standardization efforts towards 6G is slowly gaining momentum, early consideration of requirements from e-Health and Robotics verticals for 6G development is vital to contribute towards a unified 6G from the outset. A unified 6G is key towards establishing a fully digital ecosystem that can enable the realization of the use cases to its full potential as envisioned. This is crucial not only from a business perspective, but also in alleviating stress on some of the essential pillars of a well-functioning society.

 Technology
Technology